Billing Dashboard Implementation Guide
Overview
This guide explains how to implement a tenant-based real-time billing dashboard by combining the SaaSus Metering API and Pricing API, based on the sample app Billing Dashboard.
Screenshot of the billing dashboard:
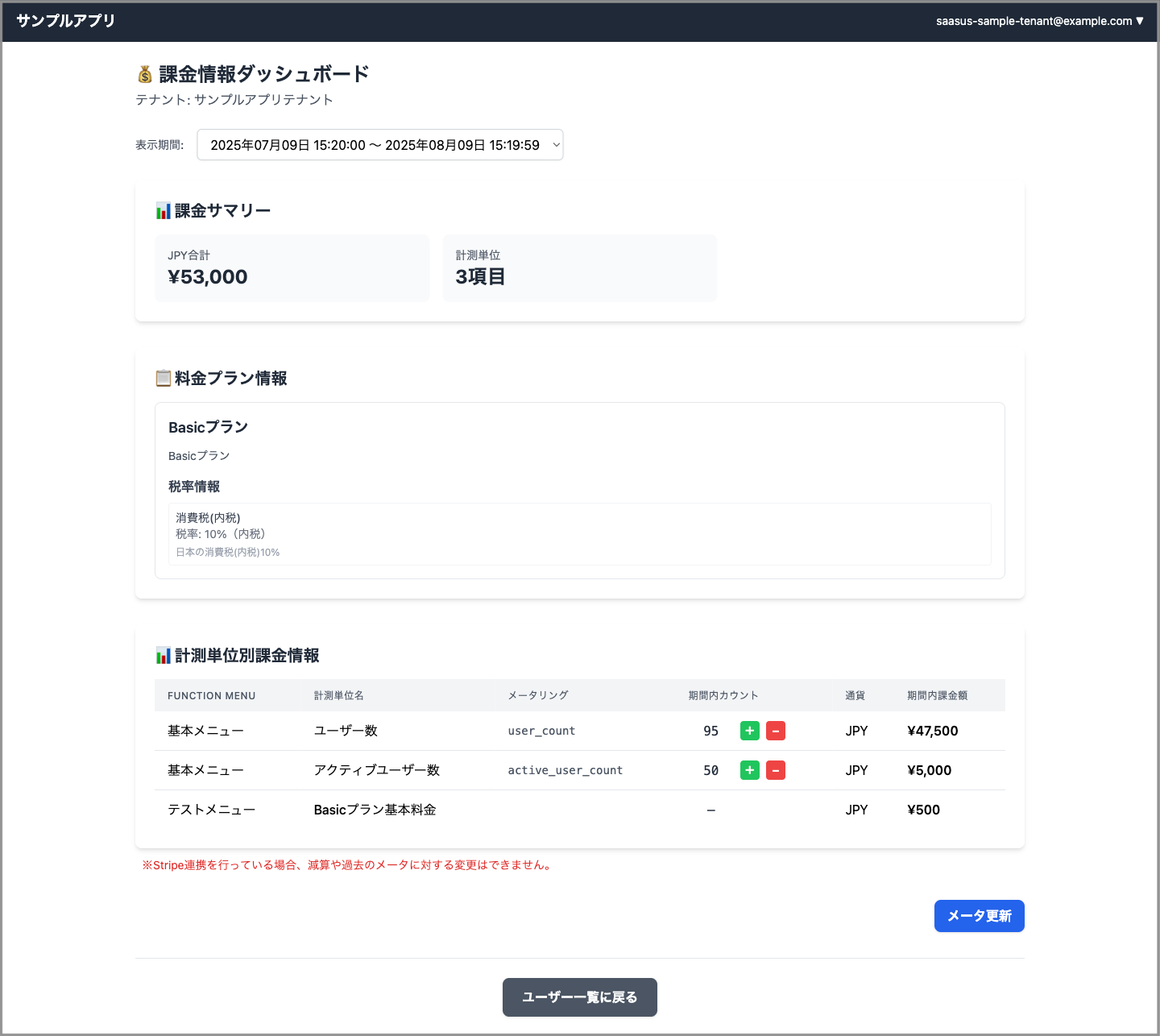
Backend Endpoint Summary
| Category | Method & Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Plan Period Candidates | GET /billing/plan_periods?tenant_id= | Returns monthly or yearly periods based on the tenant’s plan history. Used for generating a select box. |
| Dashboard Aggregation | GET /billing/dashboard | Retrieves metering summaries, billing amounts, and plan information in one response. |
| Meter Update (Current Time) | POST /billing/metering/{tenant_id}/{unit} | Applies immediate metering updates using add / sub / direct method. |
| Meter Update (Custom Timestamp) | POST /billing/metering/{tenant_id}/{unit}/{ts} | Updates metering values using a specified timestamp. Useful for corrections. |
Plan history can be obtained from the plan_histories array in the response of Get Tenant Details in the Auth API.
Plan Period Candidates Endpoint
Implementing a Period Select Box
The backend splits plan periods into monthly or yearly segments and returns labels and Unix timestamps (seconds) for the frontend.
Use the plan_histories array (which contains plan_id and plan_applied_at) from the response of Get Tenant Details in the Auth API to determine the plan application timing. Treat current_plan_period_end as the final boundary. Exclude entries with an empty plan_id.
The following implementation flow and code samples assume a Go backend and a React frontend.
Implementation Flow
- Get Tenant Info — Retrieve
planHistoriesandcurrentPlanPeriodEndfrom the Auth API. - Create Boundary Edges — Sort
planAppliedAtchronologically to formedgearray. - Define Final Boundary — Use
currentPlanPeriodEnd(or now if unavailable) minus 1 second as the final edge. - Split Periods — Determine if the interval is monthly or yearly, then generate
PlanPeriodOptionusingstep()loop. - Sort by Latest First — Sort by
Startin descending order and return to frontend.
// Step 2 & 4: Create edges and split by month/year
type edge struct { PlanID string; Time time.Time }
// ...populate edge array sorted by Time ascending...
for cur := periodStart; !cur.After(periodEnd); {
next := step(cur) // +1M for month, +1Y for year
end := next.Add(-1 * time.Second)
results = append(results, PlanPeriodOption{ Label: label(cur,end), PlanID: e.PlanID, Start: cur.Unix(), End: end.Unix() })
if end.Equal(periodEnd) { break }
cur = end.Add(time.Second)
}
On the frontend, bind these to a <select> element and refetch the dashboard on change:
// BillingDashboard.tsx (excerpt)
const fetchPeriodOptions = async () => {
const res = await axios.get<PlanPeriodOption[]>("/billing/plan_periods", { params:{ tenant_id } });
setPeriodOptions(res.data);
setSelectedPeriod(toState(res.data[0]));
};
Example Implementations
The following links point to repositories that include implementations of this endpoint.
Search by function name to locate the relevant code.
- Go (Echo):
getPlanPeriods - Python (FastAPI):
get_plan_periods - Java (Spring):
getPlanPeriods - C# (.NET 8):
GetPlanPeriods - C# (.NET Framework 4.8):
GetPlanPeriods
Dashboard Aggregation Endpoint
Difference Between max and sum in aggregate_usage
| Mode | Typical Use Case | Aggregation Method |
|---|---|---|
sum (default) | API call counts / traffic | Use total value in period |
max | Concurrent users / sessions | Use maximum value in period |
In calculateMeteringUnitBillings, the function checks aggregate_usage and uses the max or sum accordingly:
if aggUsage == "max" {
for _, c := range resp.JSON200.Counts {
if float64(c.Count) > count { count = float64(c.Count) }
}
} else { // sum
for _, c := range resp.JSON200.Counts { count += float64(c.Count) }
}
The aggregate_usage setting is only visible in the UI when Stripe integration is enabled.
It is hidden when using the platform standalone.
Billing Logic by unit_type
Metering units have a type that determines the billing logic as follows:
| type | Measurement Unit | Billing Logic |
|---|---|---|
fixed | Fixed Unit | Use fixed price as is |
usage | Usage Unit | count × price |
tiered | Tiered Unit | Add prices based on matching tier |
tiered_usage | Tiered Usage Unit | Accumulate from lower tiers upward |
func calculateAmountByUnitType(count float64, u map[string]interface{}) float64 {
unitType, _ := u["type"].(string)
price, _ := u["unit_amount"].(float64)
switch unitType {
case "fixed":
return price
case "usage":
return count * price
case "tiered":
return calcTiered(count, u)
case "tiered_usage":
return calcTieredUsage(count, u)
default:
// Fallback: treat unknown type as usage
return count * price
}
}
See calcTiered and calcTieredUsage for details.
Example Implementations
The following links point to repositories that include implementations of this endpoint.
Search by function name to locate the relevant code.
- Go (Echo):
getBillingDashboard - Python (FastAPI):
get_billing_dashboard - Java (Spring):
getBillingDashboard - C# (.NET 8):
GetBillingDashboard - C# (.NET Framework 4.8):
GetBillingDashboard
Meter Updates
The dashboard allows metering updates in two scenarios: inline edits (current time) and modal edits (specific timestamp).
Inline Edit Example (Current Time)
func updateCountOfNow(c echo.Context) error {
tenantId := c.Param("tenantId")
unitName := c.Param("unit")
userInfo, _ := c.Get(string(ctxlib.UserInfoKey)).(*authapi.UserInfo)
if !hasBillingAccess(userInfo, tenantId) {
return c.String(http.StatusForbidden, "Insufficient permissions")
}
var body struct {
Method string `json:"method"` // add | sub | direct
Count int `json:"count"`
}
if err := c.Bind(&body); err != nil {
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "invalid JSON body")
}
if body.Count < 0 {
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "count must be >= 0")
}
method := pricingapi.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountMethod(body.Method)
switch method {
case pricingapi.Add, pricingapi.Sub, pricingapi.Direct:
// OK
default:
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "method must be add, sub, or direct")
}
param := pricingapi.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountNowParam{
Method: method,
Count: body.Count,
}
resp, err := pricingClient.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountNowWithResponse(
c.Request().Context(), tenantId, unitName, param,
)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("pricing API error: %v", err)
return c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "pricing API error")
}
if resp.JSON200 == nil {
return c.String(resp.StatusCode(), string(resp.Body))
}
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, resp.JSON200)
}
The inline plus/minus buttons are only displayed when the selected period is currently ongoing.
Example Implementations
The following links point to repositories that include implementations of this endpoint.
Search by function name to locate the relevant code.
- Go (Echo):
updateCountOfNow - Python (FastAPI):
update_count_of_now - Java (Spring):
updateCountOfNow - C# (.NET 8):
UpdateMeteringCountNow - C# (.NET Framework 4.8):
UpdateMeteringCountNow
Modal Edit Example (Custom Timestamp)
func updateCountOfSpecifiedTS(c echo.Context) error {
tenantId := c.Param("tenantId")
unitName := c.Param("unit")
tsStr := c.Param("ts")
userInfo, _ := c.Get(string(ctxlib.UserInfoKey)).(*authapi.UserInfo)
if !hasBillingAccess(userInfo, tenantId) {
return c.String(http.StatusForbidden, "Insufficient permissions")
}
ts, err := strconv.ParseInt(tsStr, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "ts must be 10-digit unix seconds")
}
var body struct {
Method string `json:"method"` // add | sub | direct
Count int `json:"count"`
}
if err := c.Bind(&body); err != nil {
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "invalid JSON body")
}
if body.Count < 0 {
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "count must be >= 0")
}
method := pricingapi.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountMethod(body.Method)
switch method {
case pricingapi.Add, pricingapi.Sub, pricingapi.Direct:
// OK
default:
return c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "method must be add, sub, or direct")
}
param := pricingapi.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountParam{
Method: method,
Count: body.Count,
}
resp, err := pricingClient.UpdateMeteringUnitTimestampCountWithResponse(
c.Request().Context(), tenantId, unitName, int(ts), param,
)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("pricing API error: %v", err)
return c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "pricing API error")
}
if resp.JSON200 == nil {
return c.String(resp.StatusCode(), string(resp.Body))
}
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, resp.JSON200)
}
Example Implementations
The following links point to repositories that include implementations of this endpoint.
Search by function name to locate the relevant code.
- Go (Echo):
updateCountOfSpecifiedTS - Python (FastAPI):
update_count_of_specified_timestamp - Java (Spring):
updateCountOfSpecifiedTimestamp - C# (.NET 8):
UpdateMeteringCount - C# (.NET Framework 4.8):
UpdateMeteringCount